오봉이와 함께하는 개발 블로그
자료구조 큐(Queue) 본문
728x90
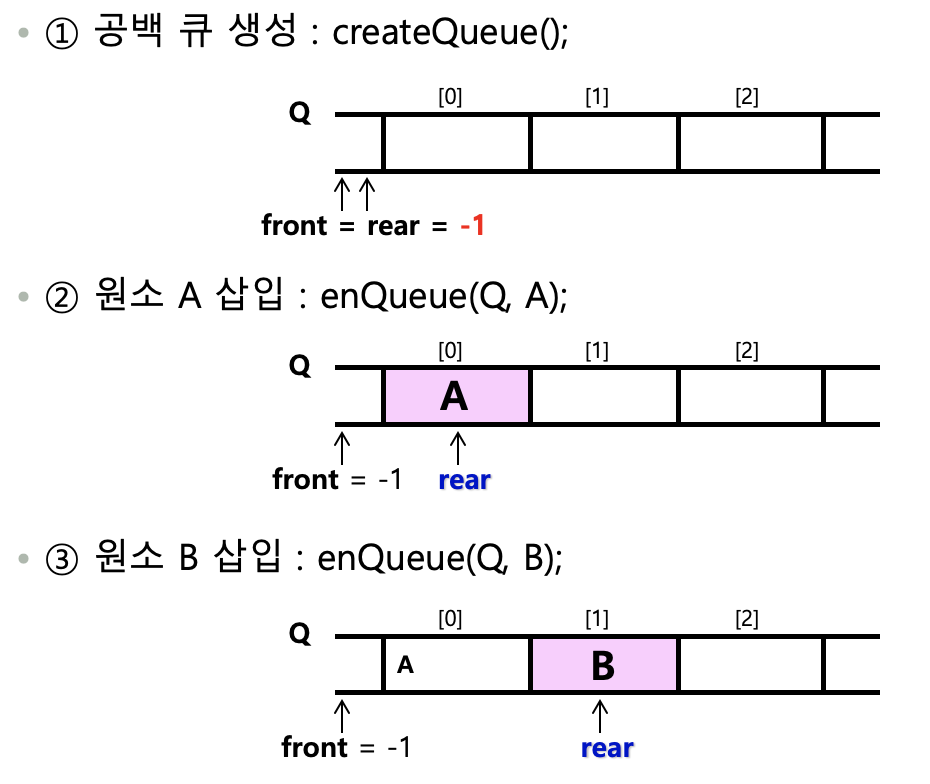
큐(Queue)
- 선형 리스트 구조의 특별한 형태
- 기억장소의 한쪽 끝에서 데이터 입력이 이루어지고, 다른 한쪽에서 데이터의 삭제가 이루어지는 구조
- 먼저 삽입한 데이터가 먼저 삭제되는 선입선출(FIFO : First In First Out)구조
- 전위 포인터(Front)
- 데이터가 삭제되는 끝을 가르키는 포인터
- 후위 포인터(Rear)
- 데이터가 삽입되는 끝을 가르키는 포인터

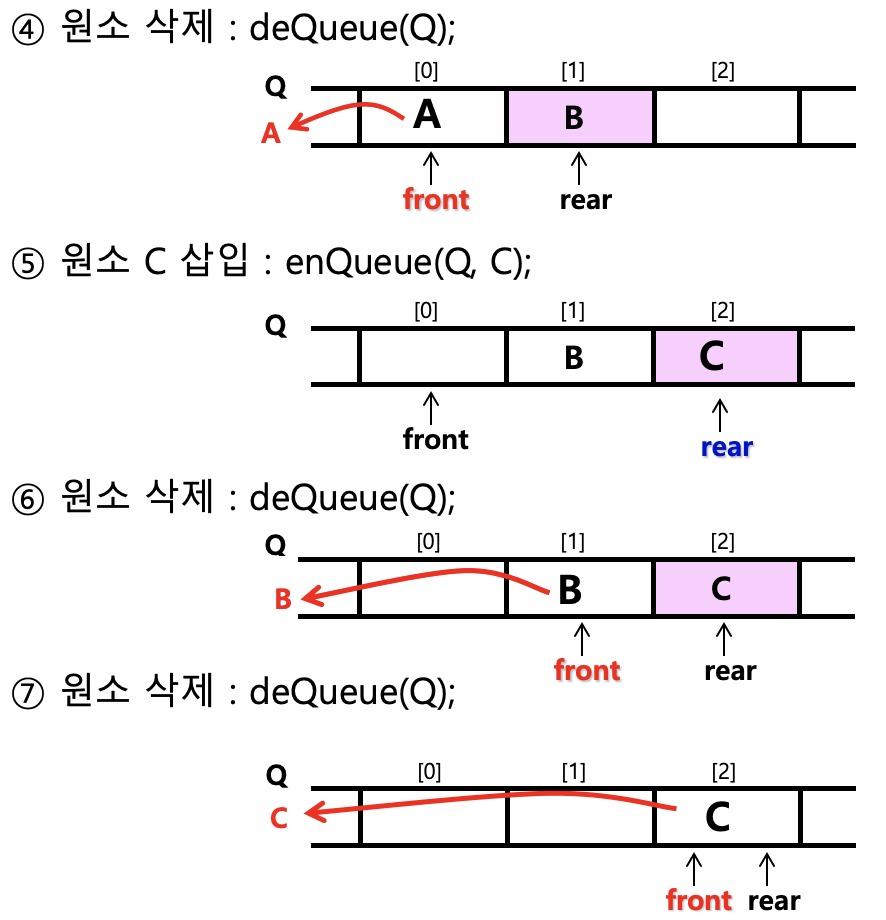
- 큐에서 오버플로우 해결 방법
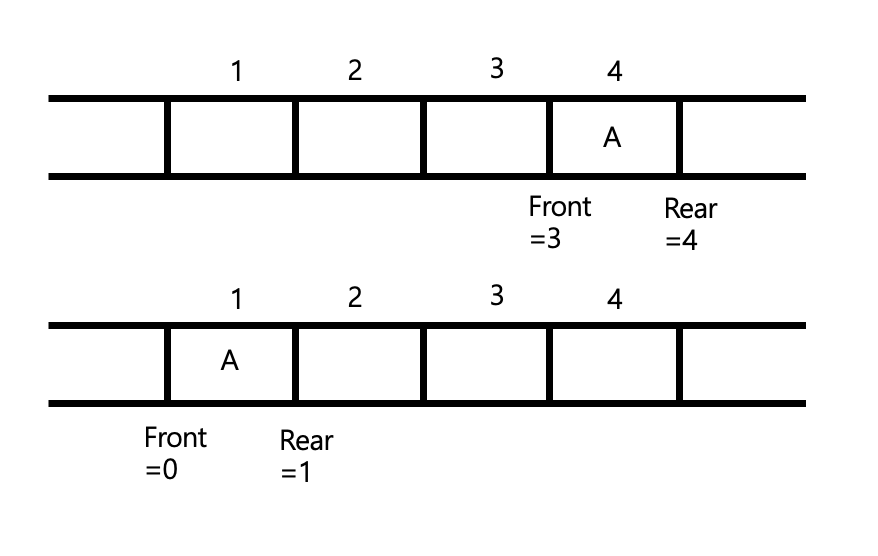
- 후위 포인터(Rear)의 값이 n(큐의 크기)과 같을 때 새로운 데이터를 삽입하면 오버폴르오 발생
- 이동 큐(moving queue) 사용
- 앞 부분이 비어 있는 경우 큐의 데이터를 앞 부분으로 이동
- 문제 : 데이터 이동에 따른 시간적 부담
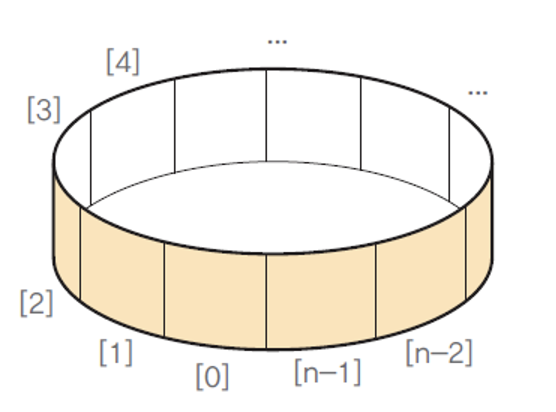
- 원형 큐(circular queue) 사용
- 선형 큐의 앞(front)과 뒤(rear)를 이어 놓은 형태의 큐
- 새로운 항목을 삽입하기 위하여 rear를 시계방향으로 증가
- 큐의 응용
- 작업 도착 순서에 의한 스케줄링
- front A - B - C - D rear
- A -> B -> C -> D 순서로 작업
큐 예제
큐 예제 1번
- 앞이 비었는데도 오버플로우 발생 : 이동 없음
MyQueue.java(배열을 통해 직접 구현 메소드)
package AlgoPractice.queue;
// 앞이 비었는데도 오버플로우 발생 : 이동 없음
public class MyQueue {
// 멤버 변수
private int queueSize; // 큐의 용량
private int front; // front -> 전위 포인터
private int rear; // rear -> 후위 포인터
private int num; // 현재 데이터 수
private char[] queue;
// 생성자에서 초기화
public MyQueue(int queueSize) {
// 배열을 사용하므로 초기값 -1로 설정
front = -1;
rear = -1;
num = 0;
this.queueSize = queueSize;
queue = new char[queueSize];
}
// 큐가 비어있는지 상태 확인 isEmpty() true / false 반환
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(front == rear) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
return true;
}
else return false;
}
// 큐가 가득 차있는 상태 확인 isFull()
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == queueSize -1;
}
// 큐에 데이터 삽입 enQueue()
// 1. Full인지 확인
// 2. 데이터 삽입
public void enQueue(char item) {
if(isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Full");
}
else {
queue[++rear] = item;
num++; // 데이터 수 증가
}
}
// 큐에서 데이터 삭제 deQueue()
// 1. Empty인지 확인
// 2. 데이터 삭제
// 3. 데이터 반환
public char deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return 'E';
}
else {
num--; // 데이터 수 감소
front++;
return queue[front];
}
}
// 큐의 첫 번째 데이터 추출하는 peek()
// 추출해서 반환
public char peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty!!! peek Failed");
return 'E';
}
else {
return queue[front+1];
}
}
// 큐 초기화 하는 clear()
public void clear() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
System.out.println("Clear!!!");
}
// 큐에 들어있는 모든 데이터 출력하는 showQueue()
// 1. 비었는지 확인
// 2. 큐애 있는 모든 데이터 출력
public void showQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty!!! showQueue Failed");
}
else {
System.out.print("Queue items : ");
for(int i = front+1; i <= rear; i++) { // front + 1 부터 rear까지
System.out.print(i + ":" + queue[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\nFront = " + (front+1) + " Rear = " + rear);
}
}
// 데이터의 갯수를 반환하는 numOfDate()
public int numOfDate() {
return num;
}
}- 배열을 통해 직접 구현(Main 메소드)
package AlgoPractice.queue;
public class MyQueueMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int queueSize = 5;
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(queueSize);
myQueue.showQueue();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueue.numOfDate() + "개");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("a, b, c enQueue");
myQueue.enQueue('a');
myQueue.enQueue('b');
myQueue.enQueue('c');
myQueue.showQueue();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueue.numOfDate() + "개");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("peek() 수행(첫 번째 값) = " + myQueue.peek());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("deQueue 수행");
System.out.println("삭제된 값 : " + myQueue.deQueue());
myQueue.showQueue();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueue.numOfDate() + "개");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("peek() 수행(첫 번째 값) = " + myQueue.peek());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("d, e enQueue");
myQueue.enQueue('d');
myQueue.enQueue('e');
myQueue.showQueue();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueue.numOfDate() + "개");
// 0은 비었고 1~4까지 데이터 4개 있음
System.out.println();
System.out.println("f enQueue");
myQueue.enQueue('f');
myQueue.showQueue();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueue.numOfDate() + "개");
// 앞 공간이 비었어도 rear가 QueueSize와 동일하기 때문에 가득 찼다고 오류 발
System.out.println();
System.out.println("clear() 수행");
myQueue.clear();
myQueue.showQueue(); // Empty
myQueue.enQueue('g');
myQueue.showQueue(); // Queue items : 0:g
}
}큐 예제 2번
- 앞이 비었기 때문에 앞으로 이동해서 오버플로우 해결
- MyQueueMove 클래스
- isFull()
- rear가 마지막 인덱스와 동일하고 데이터 수가 queueSize와 동일하면 full 상태
- enQueue()
- full 인지 확인
- 현재 Queue를 0번 인덱스부터 시작하도록 이동
- isFull()
MyQueueMove.java
package AlgoPractice.queue;
// 앞이 비었는데도 오버플로우 발생 : 해결 하는 방법
public class MyQueueMove {
// 멤버 변수
private int queueSize; // 큐의 용량
private int front; // front -> 전위 포인터
private int rear; // rear -> 후위 포인터
private int num; // 현재 데이터 수
private char[] queue;
// 생성자에서 초기화
public MyQueueMove(int queueSize) {
// 배열을 사용하므로 초기값 -1로 설정
front = -1;
rear = -1;
num = 0;
this.queueSize = queueSize;
queue = new char[queueSize];
}
// 큐가 비어있는지 상태 확인 isEmpty() true / false 반환
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(front == rear) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
return true;
}
else return false;
}
// 큐가 가득 차있는 상태 확인 isFull()
public boolean isFull() {
if ((rear == queueSize - 1) && (queueSize == num)) {
return true;
}
else return false;
}
// 큐에 데이터 삽입 enQueue()
// 1. Full인지 확인
// 2. 데이터 삽입
public void enQueue(char item) {
if(isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue Full!");
} else if(num != 0 && rear == queueSize -1){
// rear가 마지막 인덱스와 동일하지만
// 데이터가 1개라도 들어 있는 경우
// queue 이동 : 현재 queue를 복사해서
// 시작 인덱스 0으로 덮어 씀
//System.arraycopy(소스, 시작인덱스, 대상, 시작인덱스, 길이);
System.arraycopy(queue, front+1, queue, 0, queue.length - 1);
System.out.println("큐 이동 발생");
rear--;
front = -1;
queue[++rear] = item; // rear 다음 위치에 데이터 삽입
num++;
}else {
queue[++rear] = item; // rear 다음 위치에 데이터 삽입
num++; // 데이터 수 증가
}
}
// 큐에서 데이터 삭제 deQueue()
// 1. Empty인지 확인
// 2. 데이터 삭제
// 3. 데이터 반환
public char deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return 'E';
}
else {
num--; // 데이터 수 감소
front++;
return queue[front];
}
}
// 큐의 첫 번째 데이터 추출하는 peek()
// 추출해서 반환
public char peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty!!! peek Failed");
return 'E';
}
else {
return queue[front+1];
}
}
// 큐 초기화 하는 clear()
public void clear() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
System.out.println("Clear!!!");
}
// 큐에 들어있는 모든 데이터 출력하는 showQueue()
// 1. 비었는지 확인
// 2. 큐애 있는 모든 데이터 출력
public void showQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty!!! showQueue Failed");
}
else {
System.out.print("Queue items : ");
for(int i = front+1; i <= rear; i++) { // front + 1 부터 rear까지
System.out.print(i + ":" + queue[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\nFront = " + (front+1) + " Rear = " + rear);
}
}
// 데이터의 갯수를 반환하는 numOfDate()
public int numOfData() {
return num;
}
}- MyQueueMoveMain.java
package AlgoPractice.queue;
public class MyQueueMoveMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int queueSize = 5;
MyQueueMove myQueueMove = new MyQueueMove(queueSize);
myQueueMove.showQueue();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueueMove.numOfData() + "개");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("a, b, c enQueue");
myQueueMove.enQueue('a');
myQueueMove.enQueue('b');
myQueueMove.enQueue('c');
myQueueMove.showQueue();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueueMove.numOfData() + "개");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("peek() 수행(첫 번째 값) = " + myQueueMove.peek());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("deQueue 수행");
System.out.println("삭제된 값 : " + myQueueMove.deQueue());
myQueueMove.showQueue();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueueMove.numOfData() + "개");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("peek() 수행(첫 번째 값) = " + myQueueMove.peek());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("d, e enQueue");
myQueueMove.enQueue('d');
myQueueMove.enQueue('e');
myQueueMove.showQueue();
System.out.println("데이터 : " + myQueueMove.numOfData() + "개");
// 현재 큐 상태 : 0은 비었고, 1~4까지 4개 데이터가 들어 있음
// 큐 이동 없는 경우
// System.out.println("\nf enqueue 수행");
// q.enqueue('f'); // Queue Full!
// q.showQueue(); // Queue items : 1:b 2:c 3:d 4:e
// System.out.println("\n데이터 : " + q.numOfData()); // 데이터 : 4
// 앞 공간이 비었더라도 rear가 stackSize(인덱스 4, 5개)와 동일하면 오버플로우 발생
// --> 해결1 : 이동 큐, 해결2 : 원형 규
// 이동 큐
System.out.println("\nf enQueue 수행");
myQueueMove.enQueue('f'); // 큐 이동 발생
myQueueMove.showQueue(); // Queue items : 0:b 1:c 2:d 3:e 4:f
System.out.println("\n데이터 : " + myQueueMove.numOfData()); // 데이터 : 5
System.out.println("\ng enQueue 수행");
myQueueMove.enQueue('g'); // Queue Full!
myQueueMove.showQueue(); // Queue items : 0:b 1:c 2:d 3:e 4:f
System.out.println("\ndeQueue 수행");
System.out.println("삭제된 값 : " + myQueueMove.deQueue()); // 삭제된 값 :b
myQueueMove.showQueue(); // Queue items : 1:c 2:d 3:e 4:f
System.out.println("\nclear 수행 ");
myQueueMove.clear();
myQueueMove.showQueue(); // Queue Empty
System.out.println("\nh enQueue 수행");
myQueueMove.enQueue('h'); // Queue Full!
myQueueMove.showQueue(); // Queue items : 0:h
}
}큐 예제 3번
- java.util.Queue 인터페이스를 LinkedList로 구현
- ArrayList로 구현할 경우 추가/삭제 시 데이터 이동이 필요하기 때문
QueueLinkedList.java
package AlgoPractice.queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<String>();
// 큐에 값 추가
System.out.println("큐에 값 4개 삽입");
q.add("홍길동");
q.add("이몽룡");
q.add("성춘향");
q.offer("김철수");
System.out.println("\n큐의 내용 출력");
System.out.println(q); // [홍길동, 이몽룡, 성춘향, 김철수]
System.out.println(q.toString()); // [홍길동, 이몽룡, 성춘향, 김철수]
System.out.println("\n큐의 크기 : " + q.size()); //큐의 크기 : 4 (데이터 수)
System.out.println("\npeek 수행. 첫 번째 값 출력 : " + q.peek()); // 홍길동
System.out.println("\n첫 번째 값 삭제 : " + q.poll()); // 홍길동
System.out.println(q); // [이몽룡, 성춘향, 김철수]
// 또는 remove() 사용
System.out.println("\n첫 번째 값 삭제 : " + q.remove()); // 이몽룡
System.out.println(q); // [성춘향, 김철수]
// remove("검색어")는 검색해서 삭제 가능
System.out.println("\n검색한 값 삭제(없는 경우) : " + q.remove("강길동"));
System.out.println("\n검색한 값 삭제(찾은 경우) : " + q.remove("김철수"));
System.out.println(q);
}
}728x90
'알고리즘 & 자료구조 & 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 연결 리스트 - 선형 리스트 (0) | 2021.11.29 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조 데크(deQue) (0) | 2021.11.29 |
| 자료구조와 스택 (0) | 2021.11.29 |
| 동적 프로그래밍 기법 (0) | 2021.11.29 |
| Greedy기법(최단 경로, 최소 신장 트리) (0) | 2021.11.29 |
Comments




