오봉이와 함께하는 개발 블로그
Spring - 스프링 싱글톤 & 어노테이션을 통한 DI 본문
728x90
스프링 Singleton
- 스프링 컨테이너는 빈을 생성할 때 싱글톤 패턴을 적용하지 않아도 항상 클래스당 1개의 인스턴스만 생성(디폴트)
- singleton 속성 변경 가능
- <bean> 태그의 scope 속성을 이용하여 빈이 싱글톤으로 생성되게 할지 아니면 요청할 때 마다 생성되게 할지 설정 가능
- singleton : 컨테이너에 한 개의 인스턴스만 생성 (기본값)
- prototype : 빈을 요청할 때마다 인스턴스 생성
- thread : 쓰레드별로 생성
- request / session / application 스코프 있음
Annotation을 이용한 DI
- xml 설정 파일에서 <bean> 태그를 이용해서 설정하였던 빈 설정을 Annotation(메타데이터)을 이용해서 자바 코드에서 설정
- 예: xml 설정 파일에서 <bean>을 설정하지 않고
- 스프링이 자바 소스 코드를 읽어서 클래스에 @Component 어노테이션이 붙은 클래스를 객체화 (bean 설정)
- A1 클래스의 객체를 A2 클래스의 객체로 변경하려면 A1 클래스에서 @Component를 제거하고 A2 클래스에 @Component를 붙이면 됨
- @Autowired 어노테이션을 사용하여 bean을 자동 삽입
xml 설정 파일에 context 네임스페이스 추가
- 빈 설정을 위한 어노테이션을 사용하기 위해서는 설정 파일에 context 네임스페이스가 추가되어 있어야 함
- [Namespaces] 탭에서 추가
- <context:component-scan> 태그 이용하여 빈으로 등록될 클래스 패키지 지정
- 의미 : 자바 소스 코드에서 @Component로 등록된 클래스를 찾아서(scan) 클래스를 객체화(빈 설정)
스프링에서 사용하는 Annotation 종류
- DI 관련 Annotation
- xml 설정 파일에 있는 /
에 대해 DI하거나 - 자바 코드에서 생성된 bean에 대해 DI 할 수 있음
- @Autowired
- 타입을 기준으로 의존성 주입
- 스프링 빈에 의존하는 다른 빈을 자동으로 주입할 때 사용
- 스프링에서 지원
- required 속성
- 의존 객체를 주입하지 않아도 될 때 사용
- @Autowired(required=false)
- xml 파일에 <bean>이 존재하지 않아도 오류 발생하지 않음
- 디폴트 : true
- 의존 객체를 주입하지 않아도 될 때 사용
- 위치
- 필드 위에
- 생성자 위에
- Setter 메소드 위에
- @Inject
- @Autowired와 동일 (자바에서 지원)
- @Qualifier
- 특정 빈의 이름을 지정
- 동일한 interface를 구현한 클래스가 여러 개 있는 경우 사용하고자 하는 특정 빈의 이름을 지정할 때 사용
- @Resource
- @Autowired와 @Qualifier를 같이 사용하는 것과 동일
- 자바에서 지원
- pom.xml에서 <dependency> 추가
- <dependency>
- <groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
- <artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
- <version>1.3.2</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- @Autowired
- xml 설정 파일에 있는 /
- 빈 생성 관련 Annotation
- 빈 생성(설정)을 위해 클래스 위에 추가되는 어노테이션
- 클래스 이름 위에 붙이면 해당 클래스 파일에 대한 bean 자동 생성 (xml 파일에서 bean 생성하지 않음)
- 생성되는 빈의 이름은 클래스 이름에서 첫 문자만 소문자
- 예: NameService 클래스의 빈 이름은 nameService
- xml 설정 파일에서 필요한 작업
- xml 설정 파일에 context 네임스페이스 추가
- <context:component-scan base-package=”패키지명” />
- @Component 어노테이션이 적용된 클래스를 빈으로 등록
- 빈으로 등록될 클래스가 들어 있는 패키지 지정
- 상위 패키지를 지정하면 하위 패키지까지 빈으로 등록될 클래스를 찾음
- <context:annotation-config /> 필요 없음
- @Component
- 일반적인 컴포넌트로 등록되기 위한 클래스에 사용
- 클래스를 빈으로 등록(부품 등록)
- 빈 id를 지정할 수 있음
- @Component("빈 이름")
- xml의 <bean id="빈 이름">에 해당
- @Controller
- 컨트롤러 클래스에 사용 (의미론적)
- @Service
- 서비스 클래스에 사용 (의미론적)
- @Repository
- DAO 클래스 또는 Repository 클래스에 사용 (의미론적)
- Spring MVC 구성에 따른 어노테이션 사용
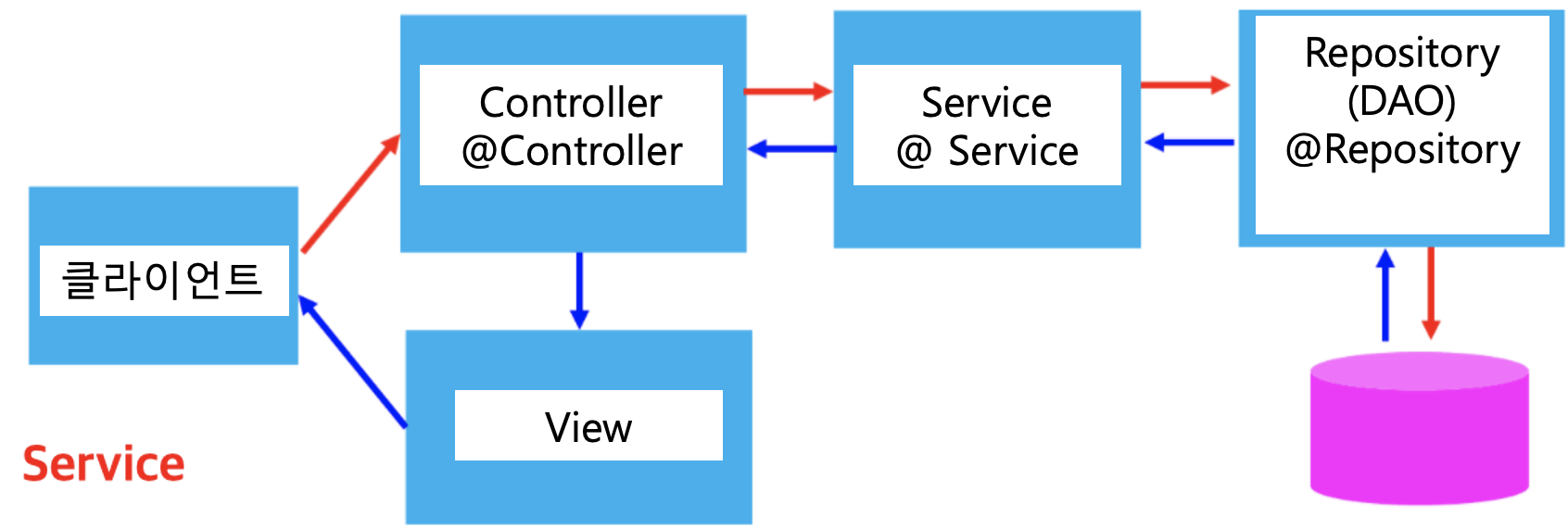
- Controller로부터 데이터 서비스를 위임 받아서 사용자의 요구 사항에 맞는 서비스 제공
- 업무 단위 또는 트랜잭션 단위로 서비스 담당
- DAO로 부터 데이터 제공 받음
- DAO를 통해서 데이터를 DB에 저장
- @Configuraton
- 빈 설정 클래스임을 나타내는 어노테이션
- @Bean
- 빈을 생성해서 반환
- 빈을 생성하는 메소드 앞에 기술
- @Bean이 붙은 메소드는 반드시 Bean 메소드 반환
- @Bean 어노테이션을 사용하는 경우
- 일반적으로 @Controller, @Service, @Repository 어노테이션을 붙이지 않는 클래스의 빈 생성에 사용
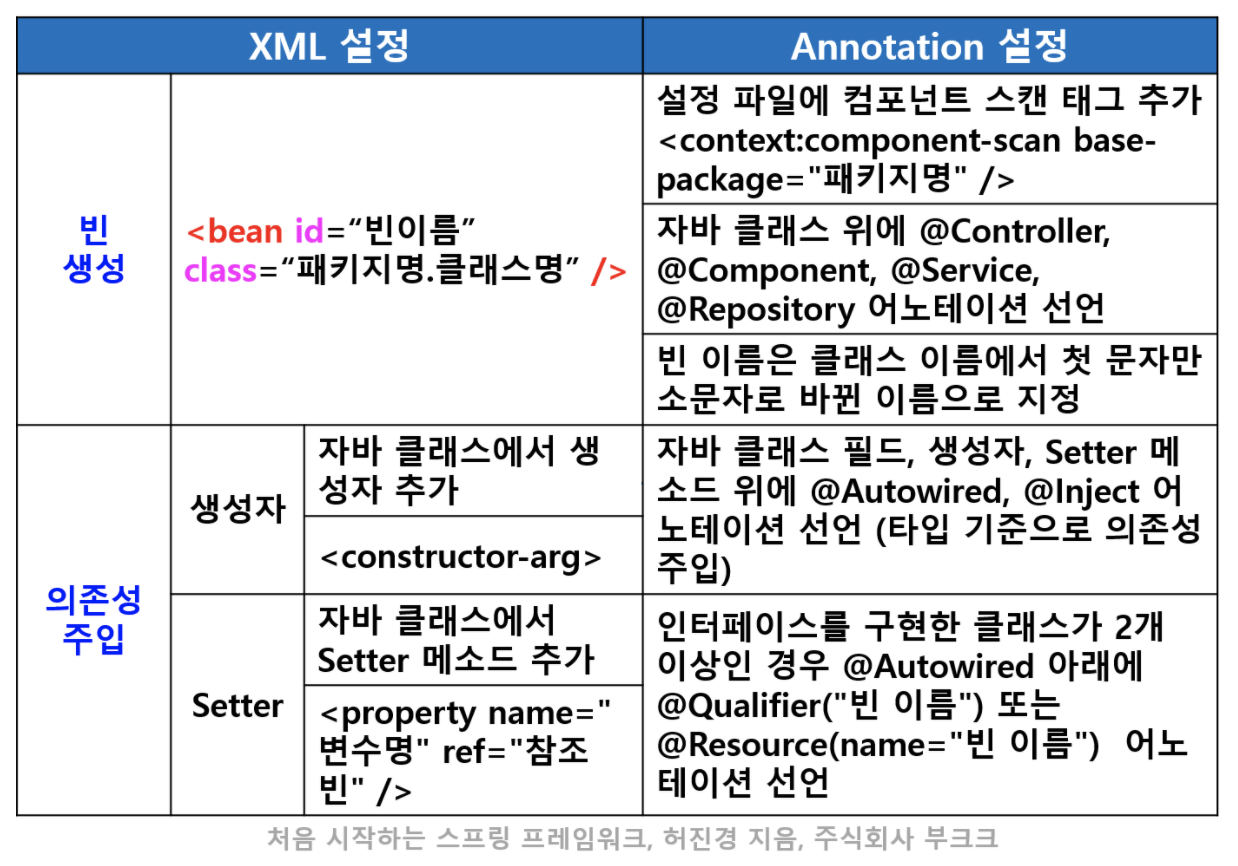
XML 설정 vs Annotation 설정
DI 관련 Annotation 예제 - applicationContext.xml, INameService.java, BNameService.java, NameController.java, AnotherNameService.java, , NameService.java, NameMain.java
- @Autowired 어노테이션 사용해서 DI 설정
- @Qualifier 어노테이션 사용해서 DI 설정
- 동일한 interface를 구현한 클래스가 여러 개 있는 경우
- 사용하고자 하는 특정 빈의 이름을 지정할 때 사용
- @Autowired 어노테이션과 같이 사용
- @Autowired
- @Qualifier("anotherNameService")
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--
...
-->
<!-- Annotation을 사용하기 위한 태그 추가 -->
<context:annotation-config />
<!-- 빈 생성 -->
<bean id="bnameService" class="com.di.spring_di_annotation.BNameService" />
<bean id="anotherNameService" class="com.di.spring_di_annotation.AnotherNameService" />
<bean id="nameService" class="com.di.spring_di_annotation.NameService" />
<bean id="nameController" class="com.di.spring_di_annotation.NameController" />
<!-- 빈만 설정하고 DI 설정 하지 않았음 -->// 인터페이스 : 규격을 정해 놓은 것
// 이 인터페이스를 구현할 클래스에서 반드시 포함시켜야 할 메소드를 규격으로 지정해 놓은 것임
public interface INameService {
// INameService 인터페이스를 구현할 클래스에서
// 반드시 오버라이드 시켜야할 추상 메소드
public String showName(String name);
}public class BNameService implements INameService {
@Override
public String showName(String name) {
System.out.println("BNameService showName() 메소드");
String myName = "내 이름은 " + name + " 입니다.";
return myName;
}
}package com.di.spring_di_annotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
public class NameController {
// 인터페이스 타입으로 선언
// @Autowired 어노테이션 사용해서 nameService 빈을 자동으로 주입
// 해당 타입의 빈을 찾아서 필드(변수)에 할당
//@Autowired
//@Qualifier("anotherNameService")
//@Qualifier("bnameService")
//@Resource(name="anotherNameService")
@Resource()
INameService nameService;
// 생성자 없음
// Setter 메소드를 통해 외부에서 주입 받음
public void setNameService(INameService nameService) {
this.nameService = nameService;
}
public void show(String name) {
System.out.println("NameController : " + nameService.showName(name));
}
}public class AnotherNameService implements INameService {
@Override
public String showName(String name) {
System.out.println("AnotherNameService showName() 메소드");
String myName = "내 이름은 " + name + " 입니다.";
return myName;
}
}public class NameService implements INameService {
@Override
public String showName(String name) {
System.out.println("NameService showName() 메소드");
String myName = "내 이름은 " + name + " 입니다.";
return myName;
}
}public class NameMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext context = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext3.xml");
// 컨테이너에서 컴포넌트(빈) 가져옴
NameController controller = context.getBean("nameController", NameController.class);
controller.show("박길동");
context.close();
}
}빈 생성 어노테이션 예제 - applicationContext4.xml, INameService.java, NameService.java, NameController.java, NameMain.java
- NameService 클래스 : 빈 생성
- @Component 어노테이션 추가
- NameController 클래스 : 빈 생성
- @Component 어노테이션 추가
- NameService 클래스 객체 사용
- NameMain 클래스
- applicationContext4.xml 사용
- NameController 클래스 객체 사용
- @Component 어노테이션을 사용하여 클래스의 빈으로 등록되었으므로 getBean() 메소드로 가져다 사용
- 설정 파일
- application-context3.xml
- xml 설정 파일에 context 네임스페이스 추가
- <context:component-scan base-package=”패키지명” />
- application-context3.xml
<context:component-scan base-package="com.di.spring_di_annotation_component" />package com.di.spring_di_annotation_component;
// 인터페이스 : 규격을 정해 놓은 것
// 이 인터페이스를 구현할 클래스에서 반드시 포함시켜야 할 메소드를 규격으로 지정해 놓은 것임
public interface INameService {
// INameService 인터페이스를 구현할 클래스에서
// 반드시 오버라이드 시켜야할 추상 메소드
public String showName(String name);
}package com.di.spring_di_annotation_component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//NameService 클래스를 빈으로 등록
// 생성된 빈 이름은 nameService
@Component
public class NameService implements INameService {
@Override
public String showName(String name) {
System.out.println("NameServie showName() 메소드");
String myName = "내 이름은 " + name + " 입니다.";
return myName;
}
}package com.di.spring_di_annotation_component;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// NameController 클래스를 빈으로 등록
// 생성된 빈 이름은 nameController
// NameMain에서 사용
@Component
public class NameController {
@Autowired
INameService nameService;
public void show(String name) {
System.out.println("NameController : " + nameService.showName(name));
}
}package com.di.spring_di_annotation_component;
import com.di.spring_di_annotation.NameController;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class NameMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext context = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("application_Context4.xml");
// 컨테이너에서 컴포넌트(빈) 가져옴
NameController controller = context.getBean("nameController", NameController.class);
controller.show("컴포넌트");
context.close();
}
}@Configuration / @Bean 어노테이션 예제 - ApplicationConfig.java, BMI.java, Member.java, MemberMain.java
package com.di.spring_di_annotation_configuration_bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.ArrayList;
@ComponentScan("com.di.spring_di_annotation_configuration_bean")
@Configuration
public class ApplicationConfig {
@Bean
public BMI bmi() {
BMI bmi = new BMI();
return bmi;
}
@Bean
public Member member() {
ArrayList<String> courses = new ArrayList<String>();
courses.add("수영");
courses.add("헬스");
courses.add("에어로빅");
Member member = new Member();
member.setBmi(bmi());
member.setName("홍길동");
member.setAge(20);
member.setHeight(170);
member.setWeight(70);
member.setCourses(courses);
return member;
}
}package com.di.spring_di_annotation_configuration_bean;
public class BMI {
public void showBMI(float height, float weight) {
float bmi = weight/(height * height) * 10000;
String result;
if(bmi >= 25) {
result = "비만입니다.";
}
else if(bmi < 25 && bmi >= 23) {
result = "과체중입니다.";
}
else if(bmi < 23 && bmi >= 18.5) {
result = "정상";
}
else {
result = "저체중";
}
System.out.println("BMI 지수 : " + bmi + " - " + result);
}
}package com.di.spring_di_annotation_configuration_bean;
import com.di.spring_di_xml_constructor_value.BMI;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Member {
private BMI bmi;
private String name;
private int age;
private float height;
private float weight;
private ArrayList<String> courses;
// 생성자 기반 DI
public Member(BMI bmi, String name, int age, float height, float weight, ArrayList<String> courses) {
this.bmi = bmi;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
this.courses = courses;
}
public BMI getBmi() {
return bmi;
}
public void setBmi(BMI bmi) {
this.bmi = bmi;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public float getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(float height) {
this.height = height;
}
public float getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(float weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public ArrayList<String> getCourses() {
return courses;
}
public void setCourses(ArrayList<String> courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
public void showBMI() {
bmi.showBMI(height, weight);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Member{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", height=" + height +
", weight=" + weight +
", courses=" + courses +
'}';
}
}package com.di.spring_di_annotation_configuration_bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class MemberMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ApplicationConfig.class);
Member member = context.getBean("member", Member.class);
System.out.println(member); // toString() 자동 호출
member.showBMI();
context.close();
}
}728x90
'BE > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring - Controller와 요청 처리 (0) | 2022.01.07 |
|---|---|
| Spring - 모델 패턴 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| Spring - AOP 간단한 기초 설명 (0) | 2022.01.05 |
| Spring - 의존성, DI(Dependency Injection) (0) | 2022.01.04 |
| Spring - 스프링 개요 (0) | 2022.01.04 |
Comments


